






 Share
Share
2025 IOF & ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium in partnership with UCM
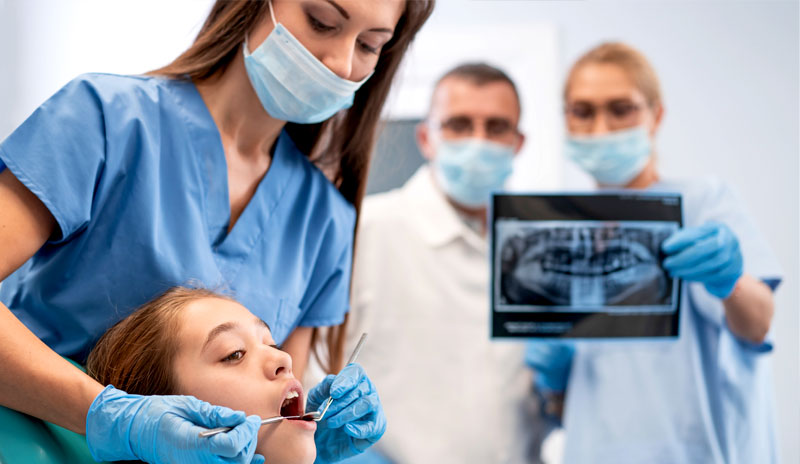
The 2025 IOF & ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium, in partnership with Complutense University of Madrid (UCM), was held in Madrid, Spain June 27th & 28th. The symposium marked a groundbreaking tri-party collaboration among Europe, Asia, and North America.
It brought together the IOF, AFI, and UCM to create a truly global platform for knowledge exchange and showcased the innovative advancements that were transforming the field of orthodontics. The program featured 30+ world-renowned speakers from over 20 leading global orthodontic institutions.
Under the theme "Emerging Technology for Interdisciplinary Care", these experts shared invaluable insights into global trends, shaped the future of orthodontics.











Highlights
• 3D Innovations and Biomechanics
• Advancements in Orthodontic and Interdisciplinary Care
• Evolution and Future of Aligner Orthodontics
• Current Trends in Orthodontic and Interdisciplinary Care
Additionally, a newly introduced New Innovator Session will feature the next generation of orthodontic leaders presenting groundbreaking ideas.
This session will also feature an exclusive update on the IOF Research Grants, which are funding real-world clinical advancements.


Introduction
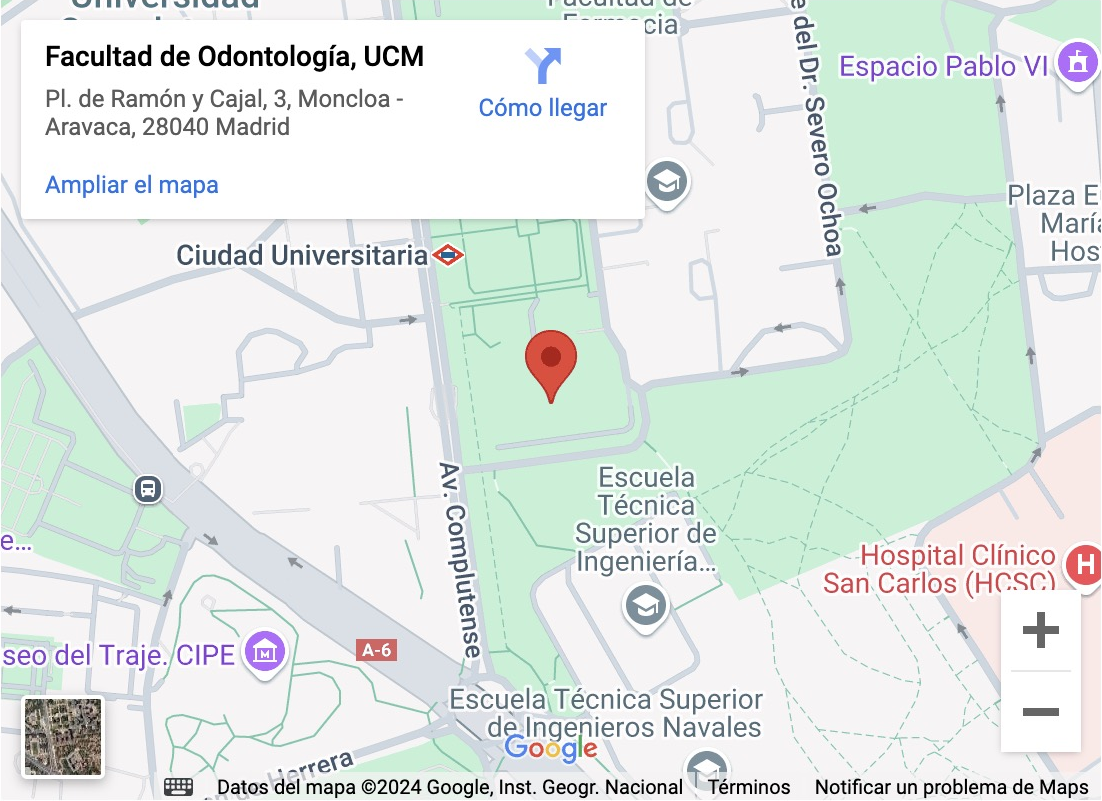
Location: Pl. de Ramón y Cajal, 3, Moncloa – Aravaca, 28040 Madrid
Date: Friday, June 27th - Saturday, June 28th, 2025 (UTC+2)
The 2025 IOF & ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium, in partnership with Complutense University of Madrid (UCM), was held in Madrid, Spain June 27th & 28th. The symposium marked a groundbreaking tri-party collaboration among Europe, Asia, and North America.
It brought together the IOF, AFI, and UCM to create a truly global platform for knowledge exchange and showcased the innovative advancements that were transforming the field of orthodontics. The program featured 30+ world-renowned speakers from over 20 leading global orthodontic institutions.
Under the theme "Emerging Technology for Interdisciplinary Care", these experts shared invaluable insights into global trends, shaped the future of orthodontics.
Organizers

International Orthodontics Foundation (IOF)
The International Orthodontics Foundation (IOF) is a not-for-profit organization devoted to improving orthodontic care around the world. The IOF enables, empowers and inspires clinicians by providing educational programs, promoting technology and innovation, and creating a global collaboration network.
With a rapidly growing global presence, IOF is inclusively open to all orthodontic clinicians. As of December 2023, we have over 13,000 members located in more than 110 countries and regions across all continents, with particular strength in North America, Europe and Asia.

The ADA Forsyth Institute
Complutense University of Madrid




Juan Carlos Palma Fernández
Wenyuan Shi
Ching-Chang Ko
Guoqiang Guan
Ben Wu
Ravindra Nanda
Guoqiang Guan
Theodore Eliades
Raffaele Spena
Oscar González-Martín

ADA Forsyth Institute designates this activity for 10 continuing education Credit. Credit are awarded on actual attendance at individual sessions.
Concerns or complaints about a CE provider may be directed to the provider or to the Commission for Continuing Education Provider Recognition at ADA.org/CERP."

Lecture Overview: Application of Clear Aligner Therapy in the Comprehensive Management of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion
This lecture will focus on the application of clear aligner therapy in the full treatment process of skeletal Class III malocclusion, from diagnosis to final outcomes. The session will provide a comprehensive overview of the orthodontic-orthognathic approach, covering key aspects of diagnosis, treatment planning, and clinical execution.
Key Topics Include:
- Differential Diagnosis of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion for Orthodontic-Orthognathic Combined Treatment
- Dental Compensation in Skeletal Class III Malocclusion
- Pre-Surgical Orthodontic Treatment Planning and Clinical Execution
- Surgical Treatment Planning for Skeletal Class III Cases
- Post-Surgical Orthodontic Management: Treatment Strategies and Clinical Procedures
- Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes This lecture will provide a systematic and practical approach to managing skeletal Class III malocclusion using clear aligners, integrating the latest advancements in digital treatment planning and multidisciplinary collaboration to optimize functional and esthetic outcomes.
- Diagnosis and Treatment Planning – Differentiating between orthodontic-orthognathic combined treatments for skeletal Class III malocclusion.
- Dental Compensation in Skeletal Class III – Understanding the compensatory mechanisms of the dentition in skeletal Class III cases.
- Pre-Surgical Orthodontic Planning and Execution – Designing and implementing pre-surgical orthodontic treatment strategies.
- Surgical Treatment Planning – Developing surgical plans tailored to skeletal Class III malocclusion cases.
- Post-Surgical Orthodontic Management – Designing and executing post-surgical orthodontic protocols.
- Treatment Outcome Evaluation – Assessing the effectiveness of treatment for skeletal Class III malocclusion.

Dental tooth autotransplantation is beginning to be a real treatment option, increasingly used in our daily practice.
Although there is scientific literature that supports this treatment, there is a general lack of knowledge on this topic. The objective of this lecture is to offer the necessary knowledge for the practice of dental tooth autotransplantation for the orthodontist in a predictable and simple way, helping us with 3D digital technology.
This lecture will include theoretical concepts of dental traumatology and tooth autotransplantation, as well as modern protocols for treating both the growing patient and the adult.
- Increasing Use of Tooth Autotransplantation – Dental autotransplantation is becoming a viable and commonly used treatment option in daily practice.
- Lack of General Knowledge – Despite scientific support, there is still limited awareness and understanding of this treatment among professionals.
- Objective of the Lecture – To provide orthodontists with the necessary knowledge to perform dental autotransplantation predictably and efficiently.
- Role of 3D Digital Technology – Modern digital tools enhance the predictability and simplicity of the procedure.
- Theoretical Foundations – The lecture covers essential concepts of dental traumatology and tooth autotransplantation.
- Treatment Protocols for Different Age Groups – The session includes protocols for managing both growing and adult patients.

- Expanded Scope of Surgery – "Orthofacial Surgery" goes beyond traditional orthognathic and facial aesthetic surgery, integrating both functional and aesthetic aspects of the facial skeleton and soft tissues.
- Shift from Cephalometric Analysis to Aesthetic Diagnosis – Surgical planning now prioritizes proportions and subjective beauty perception over numerical cephalometric measurements.
- Advancements in 3D Planning – Modern 3D technology enables precise surgical planning and execution, minimizing intraoperative improvisation.
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Principles – New surgical approaches focus on reducing tissue disruption, leading to a more empathetic and conservative intervention.
- Changing Patient Priorities – Beyond occlusion, facial aesthetics and airway considerations have become key factors driving surgical interventions.
- Paradigm Shift in Dentofacial Surgery – Traditional orthognathic surgery is considered outdated, giving rise to the more comprehensive and modern concept of "Orthofacial Surgery.

Comprehensive Malocclusion Management: Addressing OSA and Systemic Health Across Growth Phases
Upper airway obstruction in children and adolescents is commonly caused by adenoid and/or tonsillar hypertrophy, which often results in mouth breathing. This maladaptive breathing pattern can disrupt the normal development of the craniofacial complex, potentially leading to dentofacial abnormalities, including convex or concave facial profiles, in both children and adults. Additionally, upper airway obstruction in children is a significant contributing factor to the development of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which can cause growth delays, neurocognitive deficits, and even predispose children to depressive tendencies.
A multidisciplinary approach, involving orthodontics, otolaryngology, pediatrics, and other related specialties, is essential for the early diagnosis and management of upper airway obstruction. Addressing the underlying causes promptly not only aids in the prevention and correction of craniofacial malocclusions but also plays a critical role in the overall health management of the affected pediatric population. This lecture will focus on comprehensive malocclusion management throughout the growth phases, considering the implications of OSA and systemic health.
- Upper Airway Obstruction in Children and Adolescents – Often caused by adenoid and/or tonsil hypertrophy, leading to mouth breathing and potential dentofacial growth abnormalities.
- Impact on Dentofacial Development – Airway obstruction can result in abnormal convex or concave facial profiles in both children and adults.
- Association with Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) – Upper airway obstruction is linked to pediatric OSA, contributing to growth retardation, neurocognitive deficits, and even depressive tendencies.
- Importance of Multidisciplinary Collaboration – Effective management requires cooperation between orthodontics, otolaryngology, pediatrics, and other related specialties.
- Early Intervention for Comprehensive Health Management – Timely resolution of airway obstruction benefits both the prevention and treatment of malocclusions and promotes overall systemic health.

- Biomechanical Challenges of Clear Aligners – Aligners face limitations in achieving complex tooth movements, which vary across different systems.
- Research vs. Clinical Experience – While studies highlight aligners' inherent limitations, clinical evidence shows that proper protocols can enable successful treatment of complex cases.
- Mechanics of Aligner-Based Tooth Movement – The effectiveness of aligners depends on material properties, staging protocols, and force generation influenced by trimline design.
- Understanding Biomechanical Principles – Evaluating the principles that govern aligner performance helps in identifying system-specific strengths and weaknesses.
- Bridging the Research-Practice Gap – Resolving discrepancies between scientific studies and clinical outcomes allows for improved treatment predictability.
- Optimizing Treatment Planning – Insights from this analysis help refine protocols to enhance aligner therapy outcomes for better patient results.

- After this course, attendees will be able to comprehensively understand Sleep Disordered Breathing and its impacts on health, recognizing the need for prompt, effective treatment.
- After this course, attendees will be able to examine the nuances, indications, and outcomes of the primary treatment options for SDB and understand their roles, benefits, and limitations.
- After this course, attendees can develop insights into the orthodontist-patient decision-making process, learning to provide evidence-based guidance and support informed treatment choices.

Posterior bite collapse is a prevalent condition arising from tooth loss, wear, or misalignment of the posterior teeth, impacting both masticatory function and facial aesthetics. This condition can result in occlusal issues, temporomandibular joint dysfunction, and further tooth wear. The combined restorative-orthodontic treatment approach offers an effective solution to address these complications, restoring both function and aesthetics of the bite.
Historically, the treatment begins with an orthodontic phase, where tooth positions are corrected to establish proper alignment and create space for subsequent restorations. Following this, the restorative phase involves the use of dental supported restorations or implants to replace missing teeth or restore the height of worn teeth, thereby re-establishing the vertical dimension of the bite. Nevertheless, in numerous clinical scenarios, the implementation of this protocol can result in the restriction of restorative space, imprecise outcomes, and a sense of frustration. This interdisciplinary approach necessitates close collaboration between orthodontists and restorative dentists to ensure a comprehensive and harmonious outcome. In this lecture, we propose a clinical guideline to enhance this protocol, utilising objective measurements to improve the management of this specific condition.
- Posterior Bite Collapse: A common condition caused by tooth loss, wear, or misalignment, affecting both function and aesthetics. It can lead to occlusal issues, temporomandibular joint dysfunction, and further tooth wear.
- Traditional Treatment Approach: Orthodontic Phase: Aligns teeth and creates space for restorations. Restorative Phase: Uses dental-supported restorations or implants to restore vertical dimension and function.
- Challenges in Current Protocol: Potential restriction of restorative space. Variability in outcomes. Need for improved coordination between orthodontics and restorative dentistry.
- Proposed Solution: Introduction of a clinical guideline incorporating objective measurements to optimize treatment planning, improve outcomes, and enhance interdisciplinary collaboration.

In many orthodontic offices, adults and older patients represent a growing part of the customers seeking treatment. When dealing with these patients, special attention is needed because they may have complex malocclusions, require easy and esthetic treatments, and desire unrealistic results.
In recent years, new protocols, appliances and materials have provided solutions to the problems often found in adult persons and to the requests made by these patients. Aligners, lingual braces, miniscrews, are among these. However, troubles and complications may be sometimes or often met. They may be caused by the complexity of the initial problem, the compromise imposed by the patient, the response to the treatment, the compliance of the patient. Alternative solutions still need to be kept in our armamentarium to have successful treatment.
This presentation, although limited in time, will try to show how to improve treatment and final results and reduce the issues with the aid of personal “out of the ordinary” interdisciplinary protocols and the help of good coworkers.
- Increasing Demand for Adult Orthodontic Treatment – Adults and older patients represent a growing portion of orthodontic cases, often presenting with complex malocclusions and high aesthetic expectations.
- Challenges in Adult Treatment – Special considerations include case complexity, patient-driven compromises, treatment response, and compliance issues.
- Advancements in Treatment Options – New protocols, appliances, and materials such as aligners, lingual braces, and miniscrews provide solutions for adult orthodontic cases.
- Potential Complications – Troubles may arise due to the complexity of the malocclusion, patient limitations, and unpredictable responses to treatment.
- Importance of Alternative Solutions – Keeping a range of treatment options in the orthodontic armamentarium is crucial for achieving successful outcomes.
- Role of Interdisciplinary Approaches – Using innovative protocols and collaborating with skilled colleagues can enhance treatment results and minimize complications.

This presentation will explore current innovations in aligner orthodontics, focusing on advances in biomechanics and troubleshooting, and will examine future directions driven by emerging technologies. Recent research has significantly improved our understanding of the force distribution, material properties and clinical efficacy of aligners. Modern biomechanical principles are now integral to the design of treatment protocols that maximise precise tooth movement while minimising adverse effects. Through iterative testing and digital simulation, clinicians are better equipped to address common challenges such as inadequate torque control and unpredictable aligner fit, ensuring a more reliable treatment outcome.
Looking ahead, the integration of large-scale 3D printing will revolutionise aligner production by enabling mass customisation and reducing manufacturing time. In addition, the advent of metabolomics studies is paving the way for extreme personalisation in treatment planning, enabling tailored approaches that take into account individual metabolic profiles and biological responses. In parallel, advances in biocompatible and biodegradable materials promise not only improved patient comfort and safety, but also reduced environmental impact. By synthesising these interdisciplinary innovations, this presentation provides a comprehensive overview of current practice and outlines a transformative vision for the future of aligner orthodontics, where precision, efficiency and personalised care converge to redefine clinical excellence.
- Advancements in Aligner Biomechanics – Improved understanding of force distribution, material properties, and clinical efficacy enhances precise tooth movement while minimizing adverse effects.
- Troubleshooting Common Challenges – Iterative testing and digital simulation help address issues such as inadequate torque control and unpredictable aligner fit.
- Future of 3D Printing in Aligner Production – Large-scale 3D printing enables mass customization and faster manufacturing of aligners.
- Personalized Treatment through Metabolomics – Emerging research on metabolic profiles and biological responses allows for highly individualized orthodontic planning.
- Innovation in Materials – Advances in biocompatible and biodegradable materials improve patient comfort, safety, and environmental sustainability.
- Transformative Vision for Aligner Orthodontics – The integration of biomechanics, digital technologies, and personalized care is redefining precision, efficiency, and clinical excellence in orthodontic treatment.

Bone Anchored Maxillary Protraction (BAMP) has proven to be an effective alternative for treating moderate Class III malocclusion in growing individuals. This lecture aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the indications and contraindications for BAMP treatment in patients with cleft lip and palate. To this end, clinical and research outcomes will be presented from a fifteen-year experience at a single center regarding the use of BAMP in patients with cleft lip and palate, with a follow-up period of up to five years.
Several topics will be addressed and discussed: What is the impact of BAMP on the zygoma-maxillary complex? How does BAMP treatment affect the soft tissue profile? Does BAMP treatment hinder the growth of the upper airway? Can BAMP treatment induce remodelling of the mandibular fossa? Can predictive factors for favourable results be identified? What are the typical problems and complications associated with BAMP treatment?
- Effectiveness of BAMP in Class III Malocclusion – Bone Anchored Maxillary Protraction (BAMP) is a proven alternative for treating moderate Class III malocclusion in growing patients.
- Application in Cleft Lip and Palate Patients – The lecture focuses on the indications and contraindications of BAMP specifically for patients with cleft lip and palate.
- Long-Term Clinical and Research Outcomes – Insights are drawn from a 15-year single-center experience with follow-ups of up to five years.
- Impact on Craniofacial Structures – BAMP’s influence on the zygoma-maxillary complex and soft tissue profile will be discussed.
- Effects on the Upper Airway – Evaluation of whether BAMP treatment affects upper airway growth.
- Mandibular Fossa Remodeling – Investigation into whether BAMP induces changes in the mandibular fossa.
- Predictive Factors for Success – Identification of factors that may contribute to favorable treatment outcomes.
- Potential Problems and Complications – Discussion of common challenges and complications associated with BAMP treatment.

- Molar Distalization with Clear Aligners: A critical application for clear aligners in orthodontics, used to gain space, relieve crowding, or reduce dental arch protrusion.
- Higher Efficiency in Crowding Cases: Clear aligners achieve molar distalization more effectively when resolving crowding than when reducing protrusion.
- Arch Expansion Effect: The material properties of clear aligners often lead to unintended over-expansion of the dental arch, which can contribute to space creation for crowding resolution or retraction.
- Role of Skeletal Anchorage: Mini-screw anchorage significantly improves maxillary molar distalization efficiency but does not entirely prevent anchorage loss. Palatal direct mini-screw anchorage provides superior biomechanical performance.

The application of aligners in the clinical routine has followed the general pattern of introduction of new devices and materials in Orthodontics, which features a wide scale use prior to establishing evidence on their use. The challenges arising after the initial hype associated with their use, are:
- to address the constrained ability of the appliance to provide various stiffness variants across the arch outside of the limited alteration of thickness-induced hardness and stiffness;
- to handle the necessity of weekly change of aligners, owing to their lack of wide range of tooth movement, which increases attrition and wear for every new set resulting in parts of plastic ending in the GI tract;
- improve the force relaxation pattern, which impacts on the efficiency to apply steady forces over the prescribed duration;
- decrease the release of biologically-active compounds including hydrolyzed constituents of composite attachments and/or aligner-deriving monomers; and
- assess the potential release of micro- and nanoparticles.
The lecture provides a basis to address some of the foregoing issues of by introducing a modification of the synthesis and fabrication of 3D-printed aligners, which would increase the crosslinking of the polymer, enhance the stiffness and hardness of selective areas of the arch, and reduce release.
- Early Adoption vs. Evidence-Based Use: Aligners have been widely adopted in orthodontics before comprehensive evidence on their effectiveness was established.
- Challenges with Current Aligners: Limited Stiffness Variability: Aligners primarily rely on thickness changes to modify hardness and stiffness, restricting their biomechanical capabilities. Frequent Replacement Issues: Weekly aligner changes lead to increased material wear, contributing to plastic ingestion. Force Relaxation Concerns: The inability to maintain steady forces over time affects treatment efficiency. Release of Biologically-Active Compounds: Degradation of composite attachments and aligner materials may introduce bioactive substances. Microplastic and Nanoparticle Exposure: The potential release of small particles from aligners needs further assessment.

- CBCT in Clear Aligner Treatment: Enhances precision by providing a 3D view of teeth, jaw, and surrounding structures. Improves aligner fit, predictability, and potential treatment comfort.
- Role of 3D Biomechanics in Treatment Planning: Essential for managing movements in the transverse, sagittal, and vertical dimensions. Applied in both orthopedic and orthodontic treatments.
- Clinical Applications: Use of MARPE appliances for orthopedic expansion. Clear aligners for controlled orthodontic tooth movement. Case studies will illustrate biomechanics in all three planes of space.

- Causes of molar impaction include obstruction, ankylosis, insufficient space, abnormal eruption pathways, primary failure of eruption, or unknown factors.
- Impacted molars can lead to abnormal root morphology, damage to adjacent structures, and asymmetric dental and skeletal relationships.
- Clinical decisions are often based on individual case reports due to the rarity of these cases.
- Successful management requires a systematic, evidence-based approach with thorough diagnosis, optimal timing, and strategic surgical and orthodontic planning.
- The lecture will cover the management of ectopic first molars, ankylosed molars, and mesioangulated second molars.
- Discussion will include focused surgical techniques and a structured, literature-based surgical algorithm.
- Aesthetic, functional, and emotional considerations will be addressed in treatment planning.
- Practical insights and real-world strategies will be provided to enhance clinical confidence in managing complex molar impaction cases.

- Orthodontic tooth movement has been studied using various methodologies, from visual analogs to finite element analysis and micro molecular approaches.
- Research has primarily focused on enhancing the speed of tooth movement, minimizing root resorption, and optimizing force and moment delivery.
- Studies have examined both traditional braces and aligners in improving treatment efficiency.

This presentation focuses on the responses of soft and hard supporting tissues to orthodontic mechanical loading in relation to the different orthodontic techniques currently available to the orthodontist.
In order to achieve tooth movements with bone, it is necessary to distribute forces as evenly as possible along the length of the root, as occurs during translation movements.
The achievement of these movements requires good control of root movement. Careful analysis of the literature, suggests that root movements with therapy via clear aligners are not as effective as those achieved with fixed therapy and consequently the generation of translatory movements with bone are also less likely.
The still few scientific data comparing the bone changes generated by fixed appliance therapy and clear aligners even suggest a compromised capability of the latter to achieve adequate palatal root movement, potentially being able to generate labial fenestrations.
No structured data are currently available to support the hypothesis that aligner therapy is able to achieve bone changes/modeling differently than fixed appliance techniques, but as root control is more difficult, difficult also is the generation of movement with bone. Further clinical trials are needed to confirm this hypothesis.
My presentation can lead to a discussion in several directions:
- The role of industry in the spreading of knowledge and, as a consequence,
- The role of education in the spreading of knowledge
- Other possible tools to improve bone modification excluding surgery (this will involve probably also dr. Spena)
- Fixed appliances provide better root control and more effective translatory movements with bone than clear aligners.
- Clear aligners may struggle with adequate palatal root movement, potentially causing labial fenestrations.
- No conclusive evidence supports aligners modifying bone differently from fixed appliances.
- More clinical trials are needed to confirm the impact of aligners on bone changes.
- The role of industry, education, and non-surgical methods in improving bone modifications warrants further discussion.

- Orthodontic treatment for missing teeth involves either space closure or space opening for prosthetic replacement.
- Bodily tooth movement with clear aligners is challenging, especially for molars, which tend to tip rather than move bodily.
- Anchorage demands and potential side effects of intermaxillary elastics, such as midline shift, arch rotation, and jaw discrepancy, must be carefully managed.
- Orthodontic mini-implants can help prevent anchorage loss, with the anterior palate offering superior stability compared to alveolar and IZC regions.
- The combination of palatal mini-implants with the Mesialslider appliance and customized aligners can facilitate non-compliance space closure, either in a single-phase or two-phase approach.

- Utilize the seamless workflows in aligner data capture,
- Understand the use of 3D aligner software,
- Visualize the communication process with fellow clinicians,
- Plan and execute tooth movements for successful outcomes

Organizers
(Sorted alphabetically by last name)
Speakers
(Sorted alphabetically by last name)
Pl. de Ramón y Cajal
3, Moncloa – Aravaca
28040 Madrid


40 Edwin Land Boulevard, Cambridge, MA 02142
The Royal Sonesta Boston is reserved exclusively for the 2024 IOF-ADA Forsyth
International Orthodontic Symposium. You can directly arrange your
accommodation with the hotel using the link below to avail yourself of special rates.


Madrid is the capital of Spain and one of the country's largest and most vibrant cities. Known as a European cultural and artistic center, Madrid blends history and modernity with its rich heritage, art treasures, and lively lifestyle.
One of Madrid's most famous attractions is the Prado Museum (Museo del Prado), one of the world’s most important art museums, housing masterpieces by European artists like Velázquez, Goya, and Rubens. Additionally, the Reina Sofía Museum and the Thyssen-Bornemisza Museum showcase modern art and private collections, forming Madrid's "Golden Triangle of Art".
In the city center, Puerta del Sol and Plaza Mayor are must-visit spots. These squares are surrounded by traditional cafes, restaurants, and shops, offering an ideal place to experience Spanish culture. The Royal Palace of Madrid (Palacio Real), symbolizing Spanish royalty, is partially open to visitors, showcasing the luxury and history of the Spanish monarchy.
Madrid’s lifestyle is energetic, with a vibrant nightlife and a wide range of dining options, including restaurants and bars that stay open late into the night.

Event: 2025 IOF & ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium in partnership with UCM (IOS 2025)
Date: Friday, June 27th - Saturday, June 28th, 2025 (UTC+2)
USD $280 (ends on April 30th)
USD $360 (from May 1st)
USD $150 (for students only)
Payment Method: Paypal
Event: In-Person Registration
• A conference materials package
• 2 days of lunch and coffee/tea breaks
• IOF Membership: There is no cost to become an IOF member
If you need CE Credits, please visit www.iofglobal.org/ios2025, click "Registration With CE Credit" and pay an additional USD 400.
• Cancellations:
Refund requests between June 1 and June 23 will incur a $50 cancellation fee.
Requests received after June 23 will not be approved.
• Dress Code: Business Casual
• Food & Drink: Lunch and refreshments during the meeting will be provided for free.
• In consideration of being allowed to participate to the IOS 2025, the IOF and their authorized agents are hereby released from any damages caused or incurred in connection with these activities. I agree to indemnify and hold the IOF and their authorized agents harmless against any liabilities, including reasonable attorney's fees, arising from, or in connection with, these activities.
• Program Changes: Events Organizers have the right to amend this program, as necessary. In the event of a cancellation, Events Organizers and their affiliates are not responsible for incidental costs incurred by registrants. We recommend purchasing refundable airline tickets.
In case of any question, please contact us at member@iofglobal.org
* I read and agree with IOF's Event Policies.
* I read and agree with the Refund Policies.
Meet the experts and gain valuable insights. Join online for free or attend on-site for close interaction with thought leaders.
Don't miss out—register now and join me for this incredible event!
https://www.iofglobal.org/ios2025

Payment Channel Closure Date: June 26th, 2025
Amount: USD $400 for 10 credits
If you need to attend in person, please visit www.iofglobal.org/ios2025, click "In-Person Registration," and pay an additional USD 360.
If you need to attend in person, please visit www.iofglobal.org/ios2025, click "In-Person Registration," and pay an additional USD 360.
Payment Method: PayPal
Before June 22nd, 2025: Refund requests will incur a cancellation fee of USD 20.
Starting June 23rd, 2025: Refund requests will not be approved.
Live Broadcast (June 27th - June 28th):
Accumulate 4 hours of online learning on each day (June 27th and June 28th).
Complete and submit the survey questionnaire.
Replay Period (June 28th - July 6th):
Accumulate a total of 8 hours of online learning during the replay period.
Complete and submit the survey questionnaire.
All fees received by IOF will be fully paid to ADA Forsyth.
* I have read and agree to all the policies stated above.
Please add me to the IOF and ADA Forsyth Institute mailing list.

ADA Forsyth Institute designates this activity for 10 continuing education credits. Credits are awarded on actual attendance at individual sessions.
Concerns or complaints about a CE provider may be directed to the provider or to the Commission for Continuing Education Provider Recognition at ADA.org/CERP."
* Please add me to the IOF and ADA Forsyth Institute mailing list.
I am interested in becoming an IOF Member.

Register Information
With CE Credit
Legal Name:
Address:
Telephone Number:
Email:
Payment Results:

Register Information
Full Name:
Email:
Organization:
Event: 2025 IOF & ADA Forsyth International Orthodontic Symposium in partnership with UCM (IOS 2025)
Date: Friday, June 27th - Saturday, June 28th, 2025 (UTC+2)
We are looking forward to seeing you.































